
Laptops are especially prone to such damage. The sudden accelerating movement of the computer, especially when it is powered on, may possibly result in damage to the drive. One way to isolate low frequency vibrations is by supporting the speakers or the drive enclosure on spikes. Accordingly, such vibrations can be limited. Powerful vibrations caused near the computer, such as those caused by a subwoofer, may increase the risk of a head crash and of data corruption. Particulate reduction, if necessary, may be achieved by the use of an effective air purifier. Smoking in the presence of a computer is therefore discouraged. Tobacco smoke and other particulates in the air near a computer may adversely affect the drive.
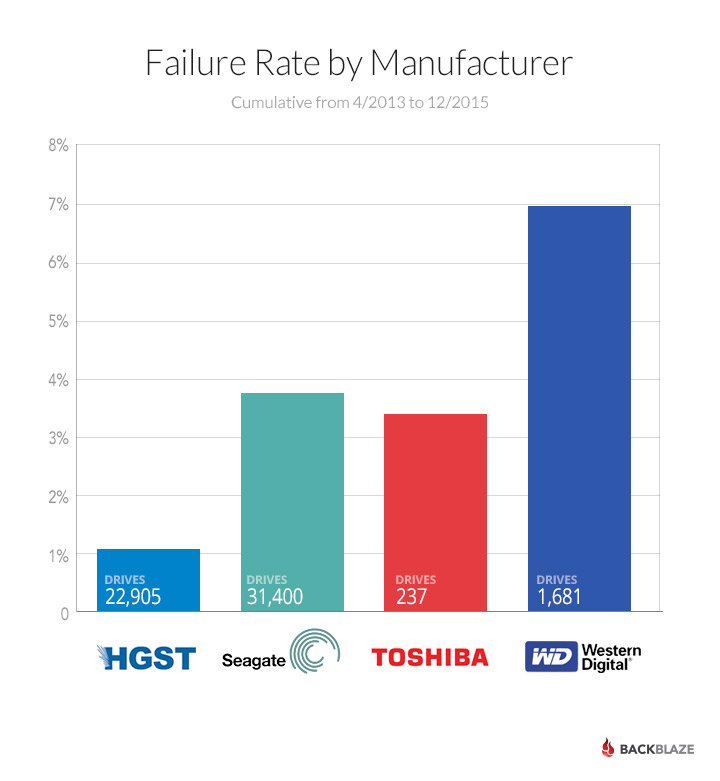
Rapid and extreme temperature changes should be avoided for this reason.Īir quality control Depending upon the change in the device's temperature, the time needed to acclimatize the device can be up to several hours. Damage can ensue if the condensation is not given sufficient time to evaporate before the device is powered on. If a computer is moved from a cold place, such as outdoors, to a relatively warm place, such as indoors, it can result in condensation inside the drive and on other system components. With such external sensors, the temperature threshold can be set to a few degrees, perhaps 5 ☌ less than that for an internal sensor.Ĭondensation control Alternatively, if the drive is in a storage backplane, the backplane may have a built-in temperature sensor with a configurable threshold. Under such situations, it might be possible to glue or tape an external temperature sensor to the drive's surface. The drive is connected to a controller card, irrespective of whether or not the card implements RAID.Especially in case of hardware-based RAID, the drive itself will not be seen by the operating system only the logical RAID drive will be seen. This is possible under at least three conditions: Unreadable sensor data Īt times, a drive may include a temperature sensor, but the temperature data may not be readable. Įven in the U.S., as is true in most engineering fields, it is highly recommended that the Celsius temperature scale be used for managing computer temperatures. The 2014 Backblaze survey of 34,000 hard drive found no correlation between temperature and failure rate. It seems inconsistent to say the failure rate increases with temperature from 10% at 44 ☌ to 6% at 55 ☌. Hard drives with average temperatures below 27 ☌ had a failure rate worse than hard drives with the highest reported average temperature of 50 ☌, and a failure rate at least twice as high as the optimum temperature range of 37 ☌ to 46 ☌. A 2007 study by Google showed the reverse to be true. If the drive includes a thermal monitoring feature, it shuts down the drive if its temperature reaches a critical level, perhaps 65 ☌.Ī common misconception is that a colder hard drive will last longer than a hotter hard drive. If the temperature exceeds a preset threshold, perhaps 50 ☌, the monitoring application can be configured to log the event, warn the user, and shut down the drive or computer. Several other programs are available as well.
#Most reliable external hard drives with low failure rates software
Two free Windows software applications that do this are HD Tune and SpeedFan in Linux the hddtemp command can be used. The sensor can be queried using software and the drive's current temperature can be steadily monitored. Several drives include a temperature sensor and a thermal monitoring feature. Stacking multiple external drives together, especially if they do not have fans, is strongly discouraged as it impedes heat transfer. An absence of a fan in the enclosure can be partly compensated for by using an ordinary table fan to improve airflow around the enclosure. This can be especially important if the drive's temperature is high.Įxternal hard disk drives must preferably be enclosed in a disk enclosure that has a fan, rather than one without a fan. Laptops also can be cooled more using a laptop cooler, with an active cooler preferred over a passive cooler. Air conditioning can be used if the room or the area in which the computer is present becomes too hot.
Other types of computer cooling can also be used as an alternative or in addition to basic air cooling. In desktops, this can be handled by ensuring that a computer fan is installed near each drive to move hot air outside. Inadequate ventilation, especially during the summer months, can cause a drive's temperature to exceed safe levels. near the upper bound of the operating temperature are thought to have a reduced lifetime. In addition, drives that constantly run relatively hot, i.e.

If the disk's read-and-write head comes in contact with the disk's surface, a catastrophic head crash can result.Įach drive has a specified lower and upper bounded operating temperature. Overheating can cause the platters to expand. Overheating is purported to be a common cause of drive failure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
